What is gametogenesis ?
The formation and development of gametes is known as gametogenesis.
The male gametes i.e sperm and female gametes i.e ovaum or ova, are formed and mature in gametogenesis process.
Organisms bears only two types of cells
1. Somatic cells or body cells and
2. Gametic cells or sex cells
Mitosis ( equational cell division)occurs in somatic cell. These cells contain diploid number of chromosomes(2n).
The sex cells are divided meiotically ( reduction division) . They bears haploid number of chromosomes (n).
The process of development of gametes are different in male and female.
Male gametes are formed and developed in the process called spermatogenesis and female gametes in oogenesis.
Spermatogenesis
The process by which production and maturation of male gametes i.e sperm occurs is called spermatogenesis.
This process occurs in the seminifrous tubule of testes. Formation of sperms takes place from germinal epithelial lining of seminifrous tubule.
Spermatogenesis occurs in two phases
1. Proliferative and maturation phase
2. Postmeotic diffenciation phase or Spermeogenesis
1.Proliferative and Maturation phase
Multiplication phase-
When the body hits puberty, the primodial germ cell called spermatogonia,in seminifrous tubule divides mitotically to produce large number of daughter cells and then enters in meosis I.
A set of spermatogonia serve as stem cell for further production of spermatogonia.
Growth phase-
This phase comprises of only growth of spermatogonia,which makes it longest among other phases .
Sertoli cells in the seminiferus tubule provides nutrients to surrounding spermatogonia, which causes enlargement of spermatogonia in to primary spermatocytes.
Maturation phase-
The primary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis in this phase.
The first meiotic division divides the diploid (2n) primary spermatocytes in to haploid (n) secondary spermatocytes.
In second meiotic division, the secondary spermatocytes formed from meiosis I , undergoes equational division to form four spermatids(n).
2.Postmeotic division or Spermeogenesis
In this phase no further division occurs, instead metamorphosis or transformation of spermatids occurs in to spermatozoa.
The process by which transformation of spermatids into spermatozoa occurs by differentiation is called Spermeogenesis.
During this phase,
i)The polarity occurs in spermatids. One end differnciate in to head and other end thickened to form middle piece. In the middle piece mitochondria are gathered to form distal centriole.
ii)Golgi apparatus surroundes the condensed nucleus becomes acrosomal cap and the secretions of golgi forms acrosome.
iii)One centriole elongates to form tail and the excess cytoplasm phagocytosed by surrounding sertoli cells.
Spermiation
The process by which mature spermatozoa are released in to the lumen of seminiferus tubule is called spermiation.
The resulting spermatozoa have lack motility. These are transfered by testicular fluid secreted by sertoli cells in to the epididymis.
In epididymis they acquire motility.
The motility of sperm doesn't help it to transport through urethra rather muscle contraction helps in transfer.
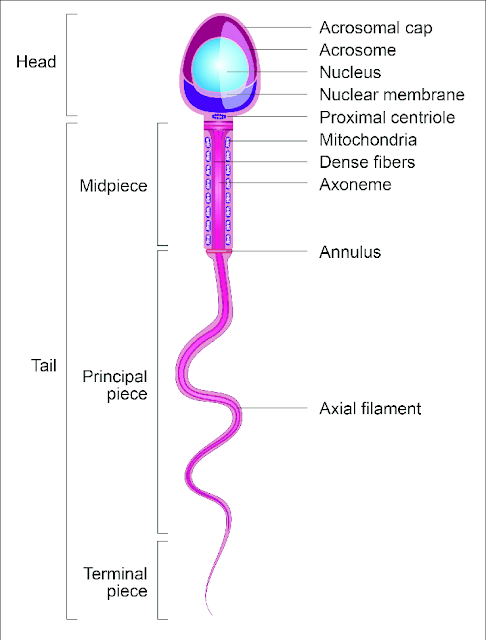
Structure of sperm
The sperm have three parts- Head,middle piece and tail.
Head - The head piece have condensed nucleus bearing 23 numbers of chromosomes.
A cap like structure called acrosome presen in head.Which bears sperm lysin enzymes like hyaluridase and proteases , helps to penitrate to secondary oocyte and drive fertilization process.
Below the head, there is a constricted region called neck,which contains centrioles in proximal end called proximal centriole and in the distal end there is distal centriole , which gives axial filament.
Middle piece- This region of sperm present below the neck region.
This contains spiral mitochondria around axial filament. The mitochondria provides energy as in the form of ATP for the tail movement and motility of sperm and helps in sperm metabolism. Below the middle piece there is tail.
Tail- The tail region has two parts. The principal piece which contains axial filament covered by fibrous seath and end piece or terminal piece which contains a necked filament.

Comments
Post a Comment