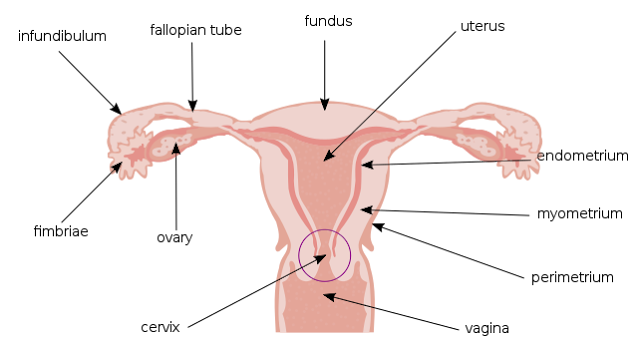
The female reproductive organs contains a pair of ovaries ,paired oviducts ( fallopian tubes), single uterus and external organs collectively called vulva.
Ovaries are the primary sex organs and others are female accessory ducts.
The ovaries secretes female sex hermones and also produce female gametes ova , the ova transport in to the fallopian tube for fertilization by sperm, implantation and development of fetus occurs in uterus, the vagina receives penis during sexual intercourse, act as a passage for menstrual flow and also the passage for child birth .
Ovaries
These are a pair of primary female reproductive organs. The ovaries are located in a shallow depression in each side of uterus called ovarian fossae and held in position within peritoneal cavity by several ligaments anchors ovary medially to the uterus.
The ovary have three parts: germinal epithelium, tunica albuginea, and ovarian stroma.
The germinal epithelium is the outer layer , which forms oogonia in the fetus.
Tunica albuginea is the layer below germinal epithelium.
Ovarian stroma has two layer-
The outer cortex contains ovarian follicle and inner vascular medulla.
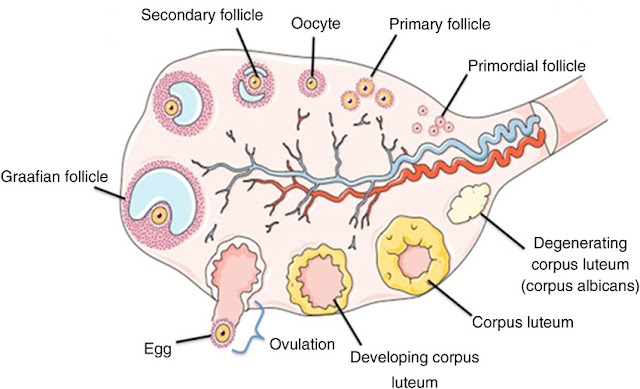
Follicular development
The ovarian follicle consists of oocytes in various stages of development with surrounding cells.
There are only 20- 40 lakh oogonia formed during birth and no further formation of oogonia occurs after birth.
The oogonia formed from germinal epithelium develop in to primary oocyte during fetal life. Then meiotic division occurs and the division arrested in prophase I of meiosis I until puberty. All eggs in primary oocyte as in diploid state ( 2n).
Each primary oocyte during arrested state surrounded by a single layer of granulosa cells called corona radiata.The primary oocyte with single layer of granulosa cell is called premodial follicle.
Granulosa cells gives nourishment for ovum keeps the ovum suspended in meiotic division.
The onset of puberty , number of primary oocyte mature each month. The enlargement of primary oocyte occurs and granulosa cell divides mitotically to form several layer of cells called cumulus oophorus.
The primary oocyte secretes a glycoprotein layer around itself called zona pellucida. Stromal cell also forms a layer called theca folliculi layer.
The granulosa cells developed microvilli with oocyte to facilitate exchange of materials. Granulosa cells keep dividing to form secondary follicle. In secondary follicle the theca layer divides into vascular theca interna ( secretes estrogen hermone) and theca externa layer .
The secondary follicle have more follicular cells and have small accumulation of fluid in intracellular space called follicular fluid.
The follicular fluid build is nutritive for oocyte and made in a cavity called antrum ( hence called antral follicle) in the center of secondary follicle in early proliferative phase.
The antral follicle develops in to a mature graafian follicle, which ruptures to release secondary oocyte. This process is called ovulation.
Corpus luteum is formed right after ovulation. It secretes estrogen, progesterone, relaxin and inhibin hermone . Corpus luteum disintegrates as Corpus albicans ,10 - 12 days after fertilization if fertilization doesn't occurs.
Graafian follicle
It is the mature ,fluid filled ovarian follicle found in mammalian ovary which release egg by the process of ovulation.
A cavity present in graafian follicle called antrum which bears follicular fluid.
Graafian follicle is also known as antral follicle due to present of antrum in it.
The oocyte in graafian follicle surrounded by granulosa cells, which secretes fluid in to the cavity.
Graafian follicle have six distinct components, theca interna, theca externa,basal lamina, granulosa cells, oocyte, and follicular fluid.
Fallopian tube
These are two muscular tubes extending from ovary up to uterus.
Its proximal end forms funnel like structure called infundibulum. The opening of infundibulum is known as ostium ,which is surrounded by number of finger- like projections called fimbriae.
The middle part of uterus is ampula, it is the longest and widest portion of uterine tube.
Isthmus is the end part of the tube which joins the uterus.
Uterus
The uterus is a hollow , muscular organs present in between urinary bladder and rectum.
It has three portions-
A dome shaped portion above the fallopian tube is fundus.
The central portion of uterus is called body, body cavity called uterine cavity.
The narrow portion that opens in to vagina is known as cervix, the interior of cervix called cervical canal. The cervical canal opens in to uterine cavity at internal orifice ( internal os) and in to vagina at external orifice ( external os).
The region between body and cervix of uterus there is isthmus, which is a constricted region.
The uterus has three layers
The outer perimetrium or serosa layer.
The middle myometrium and the inner vascular endometrium .
The endometrial layer is further divided in to two layer-
The stratum functionalis ,which sheds during menstruation and a basal layer called stratum basalis, which gives new layer of stratum functionalis after each menstruation.
Vagina
It is 10cm long , vascularised canal from cervix to exterior.
It act as passage for menstrual flow, receives penis during sexual intercourse and also acts as the passage for child birth.
The interior of vagina is lined with transverse ridges called rugae.
A thin fold of membrane present at the exterior of vagina called hymen. It may be partially cover the passage, or not present at all, in some cases ( rupture due to physical activity).
The condition in which the hymen fully covers the orifice , surgery may need to permit the discharge of menstrual flow.
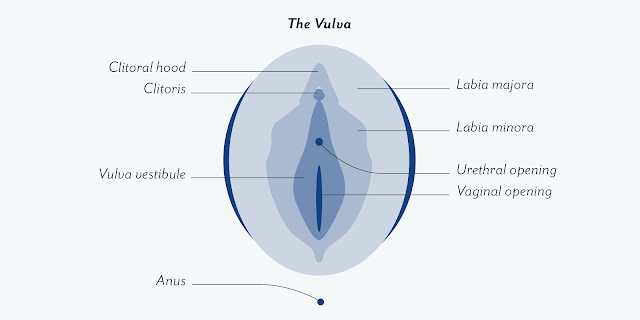
Vulva
It is the collective structure of external genital organs.
The vulva includes-
Labia majora- hair bearing fold of skin, extended from mons pubis to perineum ( the region between anus and vulva).
Labia minora- It is the small fold of skin layer below Labia majora.
Glans clitoris- It is homologus to penis in male ,which is made up of spongy tissue. During sexual arousal it becomes engorged with blood .
Urethra- Present in between vaginal orifice and clitoris.
Hermonal control
The GnRH from hypothalamus stimulates anterior pituitary to secrete LH and FSH.
The FSH stimulates development of follicle. Ripening of follicle results in increase in estrogen level, as the follicle secrets more estrogen, this gives negative feedback to pituitary to suppress the release of FSH.
As the estrogen level rises, the second pituitary hermone LH secreted ,which causes the rupture of follicle and ovulation occurs. LH convert the ruptured follicle in to corpus leuteum, which secretes progesterone and estrogen hermone.
The progesterone level negetive feedback pituitary to further release of LH.
The decline in progesterone and estrogen level again feeds back to pituitary , FSH level increases to begin the cycle again.

Comments
Post a Comment